Nexus 9k Virtual VXLAN LAB Part 3
This is the 3rd and final part of this series on building your own VXLAN Lab using ESXi and the Cisco Nexus Virtual switches.
This post will go through the creation of the VRF's for the Prod and PPD VM's and also configuring the Layer 3 VNI's for each VRF and establishing connectivity between hosts and the external network.
There are two ways in a VXLAN Fabric for traffic to be forwarded between SVI's. Inter-VLAN traffic can be either routed Asymmetrically, or Symmetrically. The Asymmetric routing path is also referred to as Bridge Route Bridge forwarding. With Asymmetric routing, say you have a host (Host A) on Leaf Switch 1 in VLAN 3012 (VNI 13012), and another host (Host B) on Leaf Switch 2 in VLAN 3014 (VNI 13014) and host A wants to send data to host B. Host A, post default gateway ARP, will send packets to its default gateway address in VLAN 3012 (Bridge). Leaf Switch 1 will then do a routing process in order to route traffic destined to VLAN 3014, out VNI 13014. Leaf Switch 2 will then receive the VXLAN packet, deencapsulated it, and bridge it over to VLAN 3014. The return traffic happens the same way, except will go over VNI 13012 instead of 13014 as host A is associated with VLAN 3012 which is attached to VNI 13012. Hence the Asymmetric routing path. Note that Asymmetric routing only works if all Leaf Switches are members of all VNIs.
Symmetric forwarding in a VXLAN fabric is when you use a layer 3 VNI to handle all of the routing of VXLAN packets between VTEPs for all VNIs. The process is the same as above however instead of sending the VXLAN packets between the Leaf Switches on their respective VNIs, all traffic is sent over the layer 3 VNI which is associated to the VRF. This lab scenario will be configured to use symmetric routing.
In order for VXLAN devices to be able to route between Layer 2 VNIs/VLANs using symmetric routing, VXLAN requires 4 things.
- A VRF
- A second (or more) L2 domain (VLAN)
- A layer 3 SVI for each of the VLANs.
- A layer 3 VNI for VXLAN traffic.
Start by configuring some basic BGP connectivity for the VXLAN fabric. The following BGP configuration is to get the Spine, Leaf, and Border Gateway devices all peering and will configure the spine switch as a BGP route reflector inside the BGP AS.
WRLABBGSW01
WRLABBGSW01(config)# conf t
WRLABBGSW01(config)# router bgp 65100
WRLABBGSW01(config-router)# router-id 10.199.210.1
WRLABBGSW01(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-af)# network 10.199.213.12/30
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-af)# template peer SPINE
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-neighbor)# remote-as 65100
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-neighbor)# update-source loopback0
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-neighbor-af)# soft-reconfiguration inbound
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-neighbor-af)# neighbor 10.199.210.2
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-neighbor)# inherit peer SPINE
WRLABSPSW01
WRLABSPSW01# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABSPSW01(config)# router bgp 65100
WRLABSPSW01(config-router)# router-id 10.199.210.2
WRLABSPSW01(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-af)# template peer LEAF
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor)# remote-as 65100
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor)# update-source loopback0
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor-af)# soft-reconfiguration inbound
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor-af)# route-reflector-client
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor-af)# neighbor 10.199.210.1
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor)# inherit peer LEAF
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor)# neighbor 10.199.210.3
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor)# inherit peer LEAF
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor)# neighbor 10.199.210.4
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor)# inherit peer LEAF
WRLABLFSW01
WRLABLFSW01# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABLFSW01(config)# router bgp 65100
WRLABLFSW01(config-router)# router-id 10.199.210.3
WRLABLFSW01(config-router)# template peer SPINE
WRLABLFSW01(config-router-neighbor)# update-source loopback0
WRLABLFSW01(config-router-neighbor)# remote-as 65100
WRLABLFSW01(config-router-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABLFSW01(config-router-neighbor-af)# soft-reconfiguration inbound
WRLABLFSW01(config-router-neighbor-af)# neighbor 10.199.210.2
WRLABLFSW01(config-router-neighbor)# inherit peer SPINE
WRLABLFSW02
WRLABLFSW02# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABLFSW02(config)# router bgp 65100
WRLABLFSW02(config-router)# router-id 10.199.210.4
WRLABLFSW02(config-router)# template peer SPINE
WRLABLFSW02(config-router-neighbor)# update-source loopback0
WRLABLFSW02(config-router-neighbor)# remote-as 65100
WRLABLFSW02(config-router-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABLFSW02(config-router-neighbor-af)# soft-reconfiguration inbound
WRLABLFSW02(config-router-neighbor-af)# neighbor 10.199.210.2
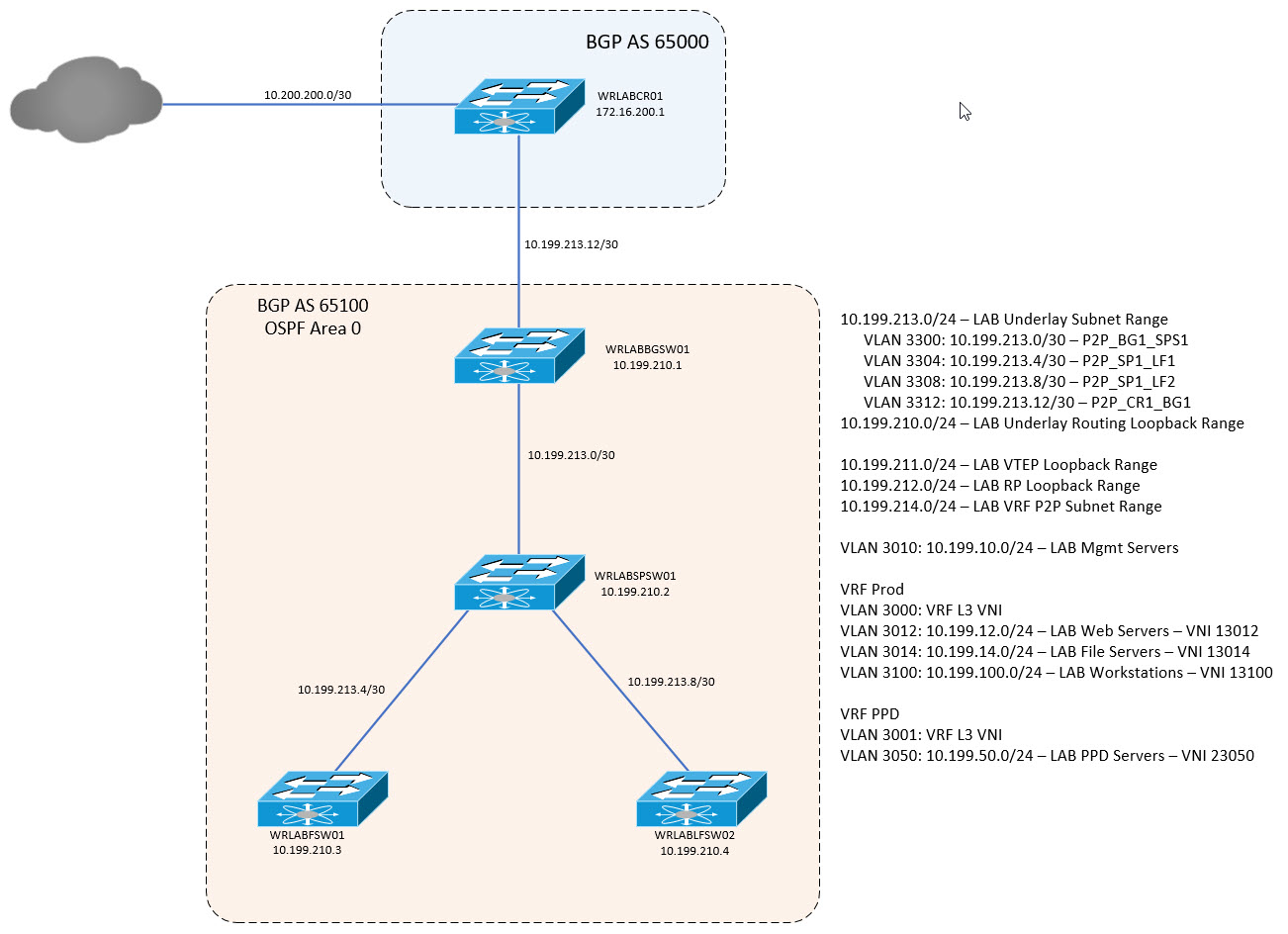
WRLABLFSW02(config-router-neighbor)# inherit peer SPINEOnce BGP has been configured on each switch, verify BGP peering from the Spine switch using the command sh bgp ipv4 uni sum. You should have BGP established from the Spine switch to the 3 BGP peers, but note that there should be no routes received yet.
With BGP done, you will need to enable the l2vpn address family in order to tell BGP to send VXLAN information and configure EVPN. This needs to be configured on each BGP peer under the peer template if you've following my configuration. Where possible I prefer to configure peer templates as I find it much easier and simpler when configuring multiple peers of the same type. Under the l2vpn address family, you will also need to configure each peer to send community values and extended community values.
WRLABSPSW01
WRLABSPSW01# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABSPSW01(config)# router bgp 65100
WRLABSPSW01(config-router)# template peer LEAF
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor)# address-family l2vpn evpn
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor-af)# send-community
WRLABSPSW01(config-router-neighbor-af)# send-community extended
Both Leaf switches and the Border Gateway switch.
# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
(config)# router bgp 65100
(config-router)# template peer SPINE
(config-router-neighbor)# address-family l2vpn evpn
(config-router-neighbor-af)# send-community
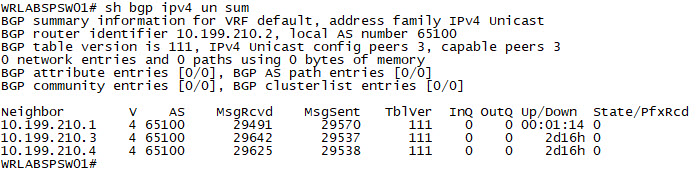
(config-router-neighbor-af)# send-community extendedWith the l2vpn address family configured, verify the peering using the command sh bgp l2vpn evpn sum. From the Spine switch you should see L2VPN peers for each of your Leaf switches and Border Gateway switches. For now, ignore that I have routes advertised/received as this is an output from a fully working VXLAN environment.
In order for VXLAN to advertise routes via BGP, you need to tell it to. As all VXLAN information is sent via the NVE interface, this is where you configure the switch to use BGP as the transport protocol. This needs to be done on any switch with a VNI attached to it in your VXLAN fabric. The following configuration is done on both Leaf switches and the Border Gateway switch in my lab.
# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
(config)# int nve 1
(config-if-nve)# host-reachability protocol bgpWith the NVE interface configured for BGP, the next step is to configure the layer 2 VNI EVPN settings. This needs to be done on both Leaf switches as these are the only switches that have the VNI's attached for the VLANs.
# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
(config)# evpn
(config-evpn)# vni 13012 l2
(config-evpn-evi)# rd auto
(config-evpn-evi)# route-target import auto
(config-evpn-evi)# route-target export auto
(config-evpn-evi)# vni 13014 l2
(config-evpn-evi)# rd auto
(config-evpn-evi)# route-target import auto
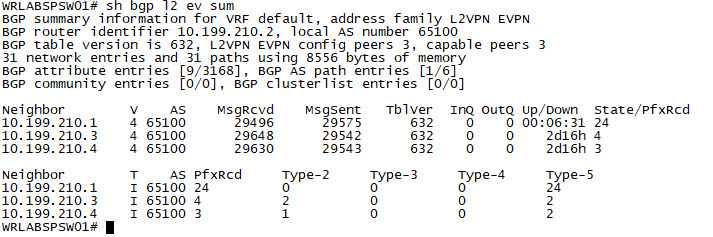
(config-evpn-evi)# route-target export autoYou should now be able to see the NVE peers and the addresses advertised via BGP.
You should also now be able to see BGP information for the Layer 2 VNI's in the output of the sh bgp l2vpn evpn command.
WRLABLFSW01# sh bgp l2vpn evpn
BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN
BGP table version is 295, Local Router ID is 10.199.210.3
Status: s-suppressed, x-deleted, S-stale, d-dampened, h-history, *-valid, >-best
Path type: i-internal, e-external, c-confed, l-local, a-aggregate, r-redist, I-injected
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete, | - multipath, & - backup, 2 - best2
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 10.199.210.3:35779 (L2VNI 13012)
*>i[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[0050.56be.73dd]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216
10.199.211.4 100 0 i
*>l[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[0050.56be.b3af]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216
10.199.211.3 100 32768 i
Route Distinguisher: 10.199.210.4:35779
*>i[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[0050.56be.73dd]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216
10.199.211.4 100 0 iOkay, now that EVPN is configured and you have connectivity within a single VNI/VLAN, it's time to configure the VRFs, and inter-vlan routing, as well as the routing between the outside network (WRLABCR01) and the VXLAN fabric. If you haven't already done so from Part 2 of this series, start by creating your second and third VLANs on the Leaf switches and then configure the NVE interface.
# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
(config)# vlan 3014
(config-vlan)# name VNI_13014
(config-vlan)# vn-segment 13014
(config-vlan)# vlan 3100
Warning: Enable double-wide arp-ether tcam carving if igmp snooping/Hsrp over vxlan is enabled. Ignore if tcam carving is already configured.
(config-vlan)# name VNI_13100
(config-vlan)# vn-segment 13100
(config-vlan)# interface nve1
Warning: Enable double-wide arp-ether tcam carving if igmp snooping/Hsrp over vxlan is enabled. Ignore if tcam carving is already configured.
(config-if-nve)# member vni 13014
(config-if-nve-vni)# mcast-group 239.0.0.14
(config-if-nve-vni)# member vni 13100
(config-if-nve-vni)# mcast-group 239.0.0.100As i mentioned in the beginning of this post, routing over VXLAN, requires a VRF. So the next step is to create the VRF so that your VXLAN switches can forward layer 3 VNI traffic. Every VRF in a VXLAN EVPN deployment must have exactly one layer 3 VNI. All traffic within that VRF, is sent via that VNI. This lab uses VLAN 3000 for the layer 3 VNI for VRF Prod, and VLAN 3001 for the PPD VRF. For now though I'm only going to create the PPD VRF and won't be configuring anything for it beyond this. The following configuration must be done on both Leaf switches, and the Border Gateway switch.
# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
(config)# vlan 3000
(config-vlan)# name L3_VNI
(config-vlan)# vn-segment 13000
(config-vlan)#
(config-vlan)# vrf context Prod
Warning: Enable double-wide arp-ether tcam carving if igmp snooping/Hsrp over vxlan is enabled. Ignore if tcam carving is already configured.
(config-vrf)# vni 13000
(config-vrf)# rd auto
(config-vrf)# address-family ipv4 unicast
(config-vrf-af-ipv4)# route-target both auto
(config-vrf-af-ipv4)# route-target both auto evpn
(config-vrf-af-ipv4)# vlan 3001
(config-vlan)# name L3_VNI_PPD
(config-vlan)# vn-segment 13001
(config-vlan)# vrf contex PPD
Warning: Enable double-wide arp-ether tcam carving if igmp snooping/Hsrp over vxlan is enabled. Ignore if tcam carving is already configured.
(config-vrf)# vni 13001
(config-vrf)# rd auto
(config-vrf)# addr ipv4 un
(config-vrf-af-ipv4)# route-target both auto
(config-vrf-af-ipv4)# route-target both auto evpnWith the VRF's created, the next step is to create the SVI for the VLAN that will be used for the Layer 3 VNI. This is so that the Layer 2 VNIs can route traffic between VTEPs. There is no need for an IP address on this SVI, it just needs to be a member of the VRF and have the command ip forward configured. Once again this needs to be configured on each device that forwards VXLAN traffic so in this lab, that means the Leaf switches and the Border Gateway switch.
# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
(config)# interface Vlan3000
(config-if)# description VXLAN L3
(config-if)# no shutdown
(config-if)# vrf member Prod
(config-if)# no ip redirects
(config-if)# ip forwardThe next step once that's all done, is to associate the VNI with the NVE interface. Once again, this needs to be done on all devices in the fabric that will forward VXLAN traffic.
(config-if)# int nve 1
(config-if-nve)# member vni 13000 associate-vrfBecause all SVI's within the VXLAN fabric have the same anycast MAC address, you need to configure the fabric forwarding settings for any-cast MAC. Once you have the any-cast MAC address configured, you need to configure each SVI and also configure the SVI forwarding mode as anycast-gateway. This configuration will be different on each of your switches depending on which SVI's are configured but also, it is only required on the switches that will forward VXLAN traffic. When configuring the SVI's, notice I've also configured the IP addresses of the SVI's with the tag 54321 command. This makes the next part of the BGP configuration easier as you will need to redistribute those connected interfaces into BGP in order to advertise the routes over the Prod VRF to the external network.
WRLABBGSW01
WRLABBGSW01# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABBGSW01(config)# fabric forwarding anycast-gateway-mac 2020.0000.00aa
WRLABLFSW01
WRLABLFSW01# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABLFSW02(config)# fabric forwarding anycast-gateway-mac 2020.0000.00aa
WRLABLFSW01(config)#
WRLABLFSW01(config)# interface Vlan3012
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# description LAB Webserver
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# no shutdown
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# vrf member Prod
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# ip address 10.199.12.1/24 tag 54321
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)#
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# interface Vlan3014
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# description LAB File servers
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# no shutdown
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# vrf member Prod
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# ip address 10.199.14.1/24 tag 54321
WRLABLFSW01(config-if)# fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
WRLABLFSW02
WRLABLFSW02# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABLFSW02(config)# fabric forwarding anycast-gateway-mac 2020.0000.00aa
WRLABLFSW02(config)#
WRLABLFSW02(config)# interface Vlan3012
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# description LAB Webserver
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# no shutdown
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# vrf member Prod
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# ip address 10.199.12.1/24 tag 54321
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)#
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# interface Vlan3014
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# description LAB File servers
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# no shutdown
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# vrf member Prod
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# ip address 10.199.14.1/24 tag 54321
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)#
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# interface Vlan3100
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# description LAB Workstations
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# no shutdown
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# vrf member Prod
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# ip address 10.199.100.1/24
WRLABLFSW02(config-if)# fabric forwarding mode anycast-gatewayThe last thing you will need to do, is configure BGP for the Prod VRF. All of the required interfaces are already configured in the correct VRF, so we just need to enable BGP for it and configure BGP to advertise the connected routes into the Prod VRF. This is required so that the hosts connected to the Fabric, will be able to reach the external network. The BGP VRF configuration, is only required on the Border Gateway switch and the Leaf Switches. The WRLABCR01 switch will not have a VRF configured.
WRLABBGSW01
WRLABBGSW01# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABBGSW01(config)# interface Ethernet1/1
WRLABBGSW01(config-if)# description P2P To WRLABCR01 E1/5
WRLABBGSW01(config-if)# no switchport
WRLABBGSW01(config-if)# vrf member Prod
WRLABBGSW01(config-if)# ip address 10.199.213.14/30 tag 54321
WRLABBGSW01(config-if)# no shutdown
WRLABBGSW01(config)# route-map VXLAN-SVI permit 10
WRLABBGSW01(config-route-map)# match tag 54321
WRLABBGSW01(config-route-map)#
WRLABBGSW01(config-route-map)# router bgp 65100
WRLABBGSW01(config-router)# vrf Prod
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-vrf)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-vrf-af)# redistribute direct route-map VXLAN-SVI
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-vrf-af)# neighbor 10.199.213.13
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-vrf-neighbor)# remote-as 65000
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-vrf-neighbor)# update-source Ethernet1/1
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-vrf-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABBGSW01(config-router-vrf-neighbor-af)# soft-reconfiguration inbound
WRLABLFSW01
WRLABLFSW01# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABLFSW01(config)# route-map VXLAN-SVI permit 10
WRLABLFSW01(config-route-map)# match tag 54321
WRLABLFSW01(config-route-map)#
WRLABLFSW01(config-route-map)# router bgp 65100
WRLABLFSW01(config-router)# vrf Prod
WRLABLFSW01(config-router-vrf)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABLFSW01(config-router-vrf-af)# redistribute direct route-map VXLAN-SVI
WRLABLFSW02
WRLABLFSW02# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABLFSW02(config)# route-map VXLAN-SVI permit 10
WRLABLFSW02(config-route-map)# match tag 54321
WRLABLFSW02(config-route-map)#
WRLABLFSW02(config-route-map)# router bgp 65100
WRLABLFSW02(config-router)# vrf Prod
WRLABLFSW02(config-router-vrf)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABLFSW02(config-router-vrf-af)# redistribute direct route-map VXLAN-SVI
WRLABCR01
WRLABCR01# conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
WRLABCR01(config)# router bgp 65000
WRLABCR01(config-router)# router-id 172.16.200.1
WRLABCR01(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABCR01(config-router-af)# neighbor 10.199.213.14
WRLABCR01(config-router-neighbor)# remote-as 65100
WRLABCR01(config-router-neighbor)# log-neighbor-changes
WRLABCR01(config-router-neighbor)# address-family ipv4 unicast
WRLABCR01(config-router-neighbor-af)# soft-reconfiguration inboundOkay, that's it. All of your fabric underlay, overlay, and VXLAN configuration should be complete. You should now be able to boot your VM's and configure an IP address, ping between them and route between SVI's inside the VXLAN fabric, as well as route to your external fabric. Verify connectivity by connecting to one of your host VM's and pinging the other Fabric host.
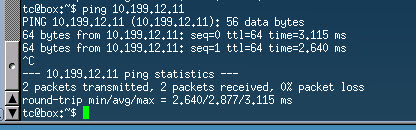
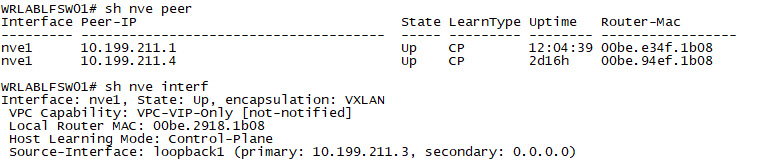
There are a number of show commands that are useful when troubleshooting VXLAN. The show nve interface, sh nve peer and the sh nve vni commands provide output related to the NVE interfaces on the switch including the neighbouring switches, and the VNIs attached to the switch.
WRLABLFSW01# sh nve interf
Interface: nve1, State: Up, encapsulation: VXLAN
VPC Capability: VPC-VIP-Only [not-notified]
Local Router MAC: 00be.2918.1b08
Host Learning Mode: Control-Plane
Source-Interface: loopback1 (primary: 10.199.211.3, secondary: 0.0.0.0)
WRLABLFSW01# sh nve peer
Interface Peer-IP State LearnType Uptime Router-Mac
--------- -------------------------------------- ----- --------- -------- -----------------
nve1 10.199.211.1 Up CP 05:21:44 00be.e34f.1b08
nve1 10.199.211.4 Up CP 2d22h 00be.94ef.1b08
WRLABLFSW01# sh nve vni
Codes: CP - Control Plane DP - Data Plane
UC - Unconfigured SA - Suppress ARP
SU - Suppress Unknown Unicast
Xconn - Crossconnect
MS-IR - Multisite Ingress Replication
HYB - Hybrid IRB mode
Interface VNI Multicast-group State Mode Type [BD/VRF] Flags
--------- -------- ----------------- ----- ---- ------------------ -----
nve1 13000 n/a Up CP L3 [Prod]
nve1 13012 239.0.0.12 Up CP L2 [3012]
nve1 13014 239.0.0.14 Up CP L2 [3014]
nve1 13100 239.0.0.100 Up CP L2 [3100] In order to view the l2vpn routes that are being advertised by BGP, use the command show bgp l2vpn evpn. This command is similar to the iipv4 command sh bgp ipv4 unicast but for VXLAN routes. As you can see the below output lists the MAC and IP addresses of hosts on the Fabric and which VTEP they are associated with.
WRLABLFSW01# sh bgp l2 ev
BGP routing table information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN
BGP table version is 895, Local Router ID is 10.199.210.3
Status: s-suppressed, x-deleted, S-stale, d-dampened, h-history, *-valid, >-best
Path type: i-internal, e-external, c-confed, l-local, a-aggregate, r-redist, I-injected
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete, | - multipath, & - backup, 2 - best2
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
Route Distinguisher: 10.199.210.1:3
*>i[5]:[0]:[0]:[24]:[10.12.10.0]/224
10.199.211.1 150 100 0 65000 ?
*>i[5]:[0]:[0]:[24]:[10.12.20.0]/224
10.199.211.1 150 100 0 65000 ?
Route Distinguisher: 10.199.210.3:35779 (L2VNI 13012)
*>i[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[0050.56be.73dd]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216
10.199.211.4 100 0 i
*>l[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[0050.56be.b3af]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216
10.199.211.3 100 32768 i
*>l[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[0050.56be.b3af]:[32]:[10.199.12.10]/272
10.199.211.3 100 32768 i
Route Distinguisher: 10.199.210.4:4
*>i[5]:[0]:[0]:[24]:[10.199.12.0]/224
10.199.211.4 0 100 0 ?
*>i[5]:[0]:[0]:[24]:[10.199.14.0]/224
10.199.211.4 0 100 0 ?
Route Distinguisher: 10.199.210.4:35779
*>i[2]:[0]:[0]:[48]:[0050.56be.73dd]:[0]:[0.0.0.0]/216
10.199.211.4 100 0 i
Route Distinguisher: 10.199.210.3:4 (L3VNI 13000)
*>i[5]:[0]:[0]:[24]:[10.12.10.0]/224
10.199.211.1 150 100 0 65000 ?
*>i[5]:[0]:[0]:[24]:[10.12.20.0]/224
10.199.211.1 150 100 0 65000 ?
*>i[5]:[0]:[0]:[24]:[10.12.30.0]/224
10.199.211.1 140 100 0 65000 ?
You can view all of your L2VPN BGP peers by using the command show bgp l2vpn evpn summary. Once again this is similar to the output of the ipv4 version of the command.
WRLABLFSW01# sh bgp l2v ev sum
BGP summary information for VRF default, address family L2VPN EVPN
BGP router identifier 10.199.210.3, local AS number 65100
BGP table version is 895, L2VPN EVPN config peers 1, capable peers 1
56 network entries and 58 paths using 13056 bytes of memory
BGP attribute entries [17/5984], BGP AS path entries [1/6]
BGP community entries [0/0], BGP clusterlist entries [2/8]
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
10.199.210.2 4 65100 4404 4316 895 0 0 2d22h 27
Neighbor T AS PfxRcd Type-2 Type-3 Type-4 Type-5
10.199.210.2 I 65100 27 1 0 0 26
WRLABLFSW01#
Below is the output of the two Linux VM ethernet interfaces showing their IP and MAC address information. As you can see in the below output, I am able to successfully ping between the two hosts.
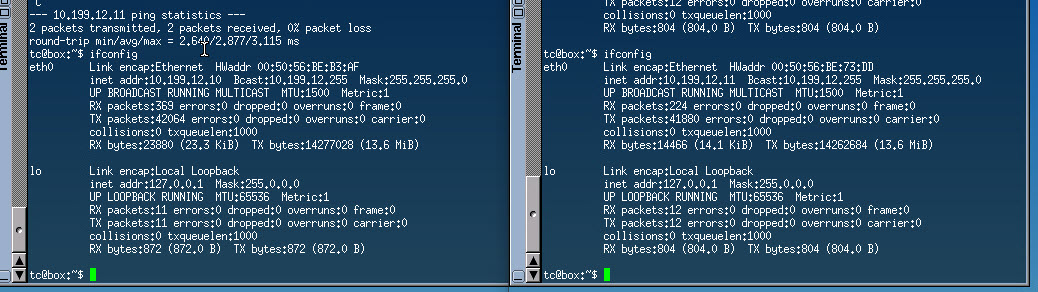 | 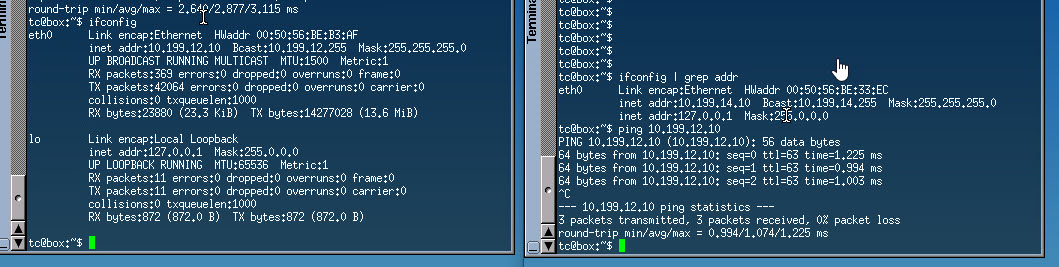 |
If you now take a look at the output of the sh bgp l2vpn evpn command on one of the Leaf Switches, you can verify the MAC and IP information that is sent by BGP and that each is associated with the correct VNI. As you can see below, Host A with MAC 00:50:56:be:d3:af is attached to L2 VNI 13012 with an IP address of 10.199.12.10, and Host B with a MAC of 00:50:56:be:33:ec is attached to L2 VNI 13014, with an IP address of 10.199.14.10.
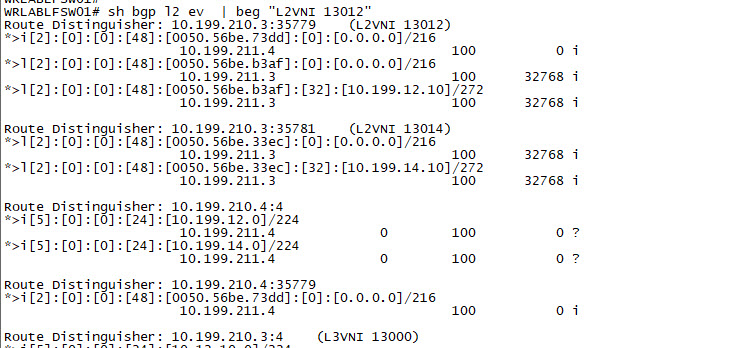
That's its for this 3 part series on VXLAN. If you've noticed anything missing or have any issues with this post, please leave a comment and let me know.
For reference, I've added the completed configuration for each device below.
Leaf1
feature scp-server
feature tacacs+
nv overlay evpn
feature ospf
feature bgp
feature ospfv3
feature pim
feature interface-vlan
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
feature nv overlay
fabric forwarding anycast-gateway-mac 2020.0000.00aa
ip pim rp-address 10.199.212.2 group-list 224.0.0.0/4
ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8
ip igmp snooping vxlan
vlan 1,3000,3012,3014,3100
vlan 3000
name L3_VNI
vn-segment 13000
vlan 3012
name VNI_13012
vn-segment 13012
vlan 3014
name VNI_13014
vn-segment 13014
vlan 3100
name VNI_13100
vn-segment 13100
route-map VXLAN-SVI permit 10
match tag 54321
vrf context Prod
vni 13000
rd auto
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-target both auto
route-target both auto evpn
interface Vlan3000
description VXLAN L3
no shutdown
vrf member Prod
no ip redirects
ip forward
interface Vlan3012
description LAB Webserver
no shutdown
vrf member Prod
ip address 10.199.12.1/24 tag 54321
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
interface Vlan3014
description LAB File servers
no shutdown
vrf member Prod
ip address 10.199.14.1/24 tag 54321
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
interface nve1
no shutdown
host-reachability protocol bgp
source-interface loopback1
member vni 13000 associate-vrf
member vni 13012
mcast-group 239.0.0.12
member vni 13014
mcast-group 239.0.0.14
member vni 13100
mcast-group 239.0.0.100
interface Ethernet1/1
description P2P To WRLABSPSW01 Eth1/2
no switchport
ip address 10.199.213.6/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/2
description WRLABTLX01
switchport access vlan 3012
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/3
description WRLABFILE01
switchport access vlan 3014
spanning-tree port type edge
no shutdown
interface loopback0
ip address 10.199.210.3/32
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback1
description VTEP Loopback
ip address 10.199.211.3/32
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
router ospf LAB
router-id 10.199.210.3
router bgp 65100
router-id 10.199.210.3
template peer SPINE
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
neighbor 10.199.210.2
inherit peer SPINE
remote-as 65100
update-source loopback0
address-family ipv4 unicast
soft-reconfiguration inbound
vrf Prod
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute direct route-map VXLAN-SVI
evpn
vni 13012 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export auto
vni 13014 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export auto
leaf 2
feature scp-server
feature tacacs+
nv overlay evpn
feature ospf
feature bgp
feature ospfv3
feature pim
feature interface-vlan
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
feature nv overlay
fabric forwarding anycast-gateway-mac 2020.0000.00aa
ip pim rp-address 10.199.212.2 group-list 224.0.0.0/4
ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8
ip igmp snooping vxlan
vlan 1,3000,3012,3014,3100
vlan 3000
name L3_VNI
vn-segment 13000
vlan 3012
name VNI_13012
vn-segment 13012
vlan 3014
name VNI_13014
vn-segment 13014
vlan 3100
name VNI_13100
vn-segment 13100
route-map VXLAN-SVI permit 10
match tag 54321
vrf context Prod
vni 13000
rd auto
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-target both auto
route-target both auto evpn
interface Vlan3000
description VXLAN L3 VNI
no shutdown
vrf member Prod
no ip redirects
ip forward
interface Vlan3012
description LAB Webservers
no shutdown
vrf member Prod
ip address 10.199.12.1/24 tag 54321
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
interface Vlan3014
description LAB File servers
no shutdown
vrf member Prod
ip address 10.199.14.1/24 tag 54321
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
interface Vlan3100
description LAB Workstations
no shutdown
vrf member Prod
ip address 10.199.100.1/24
fabric forwarding mode anycast-gateway
interface nve1
no shutdown
host-reachability protocol bgp
source-interface loopback1
member vni 13000 associate-vrf
member vni 13012
mcast-group 239.0.0.12
member vni 13014
mcast-group 239.0.0.14
member vni 13100
mcast-group 239.0.0.100
interface Ethernet1/1
description P2P To WRLABSPSW01 E1/3
no switchport
ip address 10.199.213.10/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/2
description WRLABTLX02
switchport access vlan 3012
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/3
description WRLABFILE02
switchport access vlan 3014
spanning-tree port type edge
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/4
description WRLABWS01
switchport access vlan 3100
spanning-tree port type edge
no shutdown
interface loopback0
ip address 10.199.210.4/32
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback1
description VTEP Loopback
ip address 10.199.211.4/32
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
router ospf LAB
router-id 10.199.210.4
router bgp 65100
router-id 10.199.210.4
template peer SPINE
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
neighbor 10.199.210.2
inherit peer SPINE
remote-as 65100
update-source loopback0
address-family ipv4 unicast
soft-reconfiguration inbound
vrf Prod
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute direct route-map VXLAN-SVI
evpn
vni 13012 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export auto
vni 13014 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export auto
Spine
feature scp-server
feature tacacs+
nv overlay evpn
feature ospf
feature bgp
feature ospfv3
feature pim
feature interface-vlan
ip host WRLABBGSW01 10.199.210.1
ip host WRLABLFSW01 10.199.210.3
ip host WRLABLFSW02 10.199.210.4
ip pim rp-address 10.199.212.2 group-list 224.0.0.0/4
ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8
ip pim anycast-rp 10.199.212.2 10.199.210.2
ip igmp snooping vxlan
interface Ethernet1/1
description P2P To WRLABBGSW01 E1/2
no switchport
ip address 10.199.213.2/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/2
description P2P To WRLABLFSW01 E1/1
no switchport
ip address 10.199.213.5/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/3
description P2P To WRLABLFSW02 E1/1
no switchport
ip address 10.199.213.9/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface loopback0
ip address 10.199.210.2/32
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback1
description VTEP Loopback
ip address 10.199.211.2/32
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback10
description RP Loopback
ip address 10.199.212.2/32
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
router ospf LAB
router-id 10.199.210.2
name-lookup
router bgp 65100
router-id 10.199.210.2
address-family ipv4 unicast
template peer LEAF
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
route-reflector-client
neighbor 10.199.210.1
inherit peer LEAF
remote-as 65100
update-source loopback0
address-family ipv4 unicast
soft-reconfiguration inbound
neighbor 10.199.210.3
inherit peer LEAF
remote-as 65100
update-source loopback0
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-reflector-client
soft-reconfiguration inbound
neighbor 10.199.210.4
inherit peer LEAF
remote-as 65100
update-source loopback0
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-reflector-client
soft-reconfiguration inbound
border gateway
feature scp-server
feature tacacs+
nv overlay evpn
feature ospf
feature bgp
feature ospfv3
feature pim
feature interface-vlan
feature vn-segment-vlan-based
feature nv overlay
fabric forwarding anycast-gateway-mac 2020.0000.00aa
ip pim rp-address 10.199.212.2 group-list 224.0.0.0/4
ip pim ssm range 232.0.0.0/8
ip igmp snooping vxlan
vlan 1,3000,3012
vlan 3000
name L3_VNI_13000
vn-segment 13000
vlan 3012
name VNI_13012
vn-segment 13012
route-map VXLAN-SVI permit 10
match tag 54321
vrf context Prod
vni 13000
rd auto
address-family ipv4 unicast
route-target both auto
route-target both auto evpn
interface Vlan3000
description VXLAN Layer 3
no shutdown
vrf member Prod
no ip redirects
ip forward
interface nve1
no shutdown
host-reachability protocol bgp
source-interface loopback1
member vni 13000 associate-vrf
interface Ethernet1/1
description P2P To WRLABCR01 E1/5
no switchport
vrf member Prod
ip address 10.199.213.14/30 tag 54321
no ip ospf passive-interface
no shutdown
interface Ethernet1/2
description P2P To WRLABSPSW01 E1/1
no switchport
ip address 10.199.213.1/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
no ip ospf passive-interface
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
no shutdown
interface loopback0
ip address 10.199.210.1/32
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
interface loopback1
description VTEP Loopback
ip address 10.199.211.1/32
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.0
ip pim sparse-mode
router ospf LAB
router-id 10.199.210.1
passive-interface default
router bgp 65100
router-id 10.199.210.1
address-family ipv4 unicast
network 10.199.213.12/30
template peer SPINE
update-source loopback0
address-family l2vpn evpn
send-community
send-community extended
neighbor 10.199.210.2
inherit peer SPINE
remote-as 65100
update-source loopback0
address-family ipv4 unicast
soft-reconfiguration inbound
vrf Prod
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute direct route-map VXLAN-SVI
neighbor 10.199.213.13
remote-as 65000
update-source Ethernet1/1
address-family ipv4 unicast
soft-reconfiguration inbound
evpn
vni 13012 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export auto
vni 13014 l2
rd auto
route-target import auto
route-target export auto
WRLABCR01
route-map RM-LAB-TO-OSPF permit 10
set metric 100
set metric-type type-1
interface Ethernet1/5
description P2P To WRLABBGSW01 E1/1
no switchport
ip address 10.199.213.13/30
ip ospf network point-to-point
ip ospf passive-interface
ip router ospf LAB area 0.0.0.200
no shutdown
router ospf LAB
router-id 172.16.200.1
redistribute bgp 65000 route-map RM-LAB-TO-OSPF
passive-interface default
router bgp 65000
router-id 172.16.200.1
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute ospf LAB route-map OSPF
neighbor 10.199.213.14
remote-as 65100
log-neighbor-changes
address-family ipv4 unicast
soft-reconfiguration inbound

Add new comment